
During Carolingian empire, manors in Western Europe formed a distinct structure of lords and serfs that were significant in medieval period. The manors were founded on Roman empires agricultural estates as well as the new land segmentations formed by founding medieval kings.įor instance, they existed in Mediterranean areas such as Islamic and Byzantine. The obligation could be paid through different means such as cash money or in kind (Salisbury, Joyce & Sherman, Dennis 236). This was based on vesting of the lords with both economic and legal power with regard to their power of holding large pieces of land including their legal responsibility to hold and care for the peasant persons in their area of jurisdiction. It was largely used in central and Western Europe and gradually replaced by market economies based on use of money including agrarian contracts. Manorialism on the other hand refers to an important component of feudal community which entailed the principles used in organizing economy in the rural that was born in the medieval villa system. This resulted to the development of Feudalism. Hence, Europeans assumed this arrangement by escalating European noble power from the king’s land grants in return of the services provided by the military. Traditionally, Romans ensured personal security from peasants who were submissive with considerable power to engage in warfare. Furthermore, Roman villas alongside their property were given to leaders of the military temporarily in return to their loyalty both to the emperor and to Rome (Salisbury, Joyce & Sherman, Dennis 229).
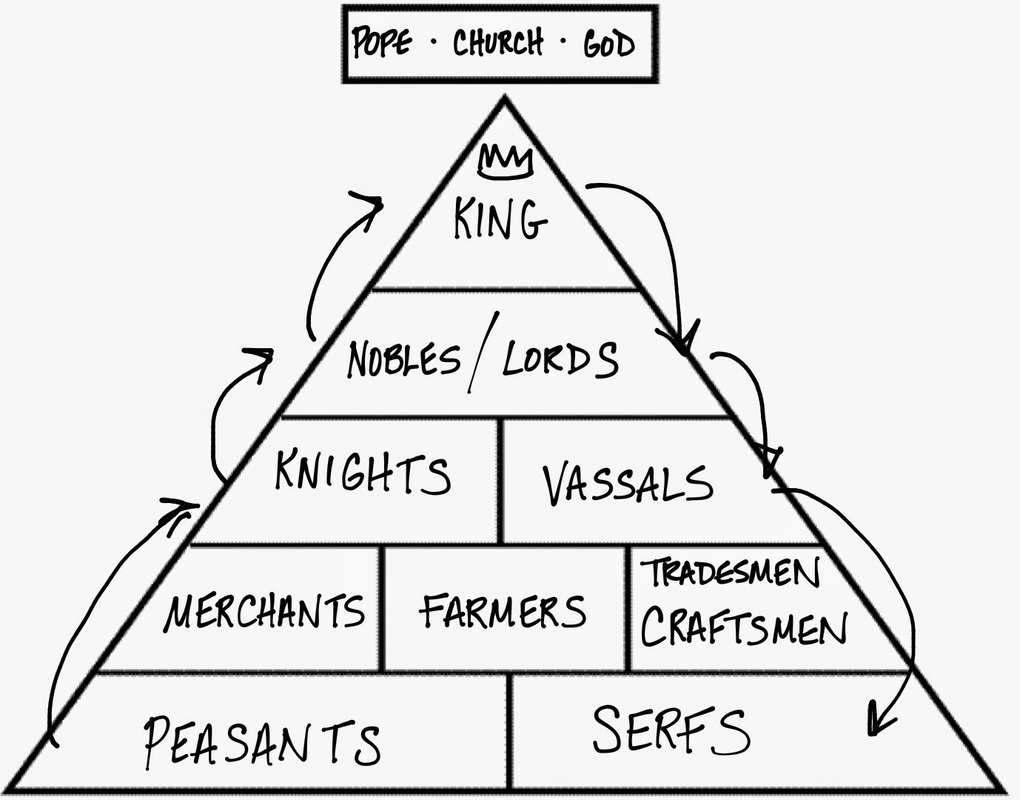
Roman regime elements were taken to military and political practices.

The initial feudalism components occurred in Germany and France in the ninth and tenth centuries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
